LILY BULB DECOCTION TO STRENGTHEN THE LUNG
Bai He Gu Jin Tang
‘Lily Bulb Decoction to Strengthen the Lung’
Source: analytic Collection of Medical Formulas (Yi Fang Ji Jie, 1682)
Keywords
pulmonary tuberculosis, tracheitis, bronchodilation, and pharyngitis
Ingredients
Rehmannia glutinosa (Sheng Di, raw rehmannia)
Rehmannia glutinosa (Shu Di, processed rehmannia)
Ophiopogon japonicus (Mai Dong, ophiopogon)
Lilium lancifolium (Bai He, lily bulb)
Paeonia sinjiangensis (Shao Yao, peony)
angelica sinensis (Dang Gui, Chinese angelica)
Fritillaria cirrhosa (Bei Mu,
fritillaria)
|Glycyrrhiza uralensis (Gan Cao, liquorice)
Scrophularia ningpoensis (Xuan Shen, scrophularia)
Platycodon grandiflorum (Jie Geng, platycodon)
Major therapeutic action
Nourishes yin, clears Heat, moistens the Lung, resolves Phlegm
antifebrile, antitussive
Indications
* Hyperactivity of deficient Fire due to yin deficiency of the Lung and Kidney.
* With the appropriate key symptoms, this formula can be used to treat biomedical conditions such as pulmonary tuberculosis, tracheitis, bronchodilation, and pharyngitis, etc.
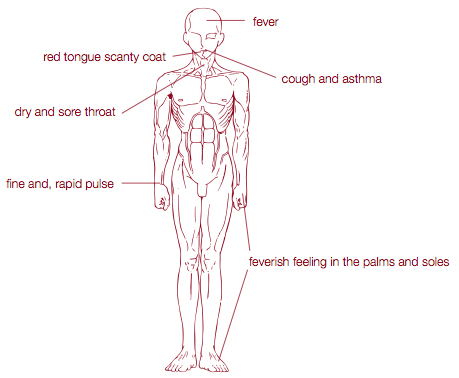
Key symptoms for use
* dry and sore throat
* cough and asthma with blood streaks in the sputum
* feverish feeling in the palms and soles
* bone-steaming fever
o red tongue with scanty fur
* fine and rapid pulse
* With low fever, combine with Bie Jia/Lycium chinensis (Di Gu Pi, lycium bark)/artemisia apiacea (Qing Hao, sweet wormwood) or Bai Wei/Lycium chinensis (Di Gu Pi, lycium bark).
The typical dose is three grams twice daily, before meals. In severe cases or the early stages of treatment (the first two weeks), a 50-100% increase in dose may be used, then reduced as the treatment takes effect.
Cautions and contraindications
None noted.
None noted.